Navigating the Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Employment Law Changes in 2024
Posted on February 5, 2024

As the new year quickly approaches, businesses, employees, and HR companies in California are bracing themselves for a wave of changes in employment laws set to take effect in 2024. Many laws will affect the entire nation, while others just pertain to specific states or localities. They cover a wide range of topics as well. From increased worker protections to evolving workplace dynamics, these amendments aim to adapt to the ever-shifting landscape of the modern workforce.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the key employment law changes that will shape the employer-employee relationship at both a Federal and State level once the new year arrives.
Federal Changes
As labor relations transform and adapt to the trends of today, the federal government is poised to introduce key amendments that will impact employers and employees alike. Below are some of the anticipated changes to federal employment laws in 2024 and their implications for the broader employment landscape.

OSHA Final Rule on Workplace Injury and Illness Reporting Requirements (29 CFR 1904)
According to 29 CFR 1904, certain employers will now be required to report injury/illness reports and other information to OSHA via electronic communication. Employers who fall into one of many different types of industries and who have more than 100 employees will now have to submit information to OSHA once a year online.
NLRB Final Joint Employer Rule
On October 26, 2023, the National Labor Relations Board (“NLRB” or “the Board”) released a final rule setting forth the standard for joint-employer status under the National Labor Relations Act (“NLRA” or “the Act”).
Need insights into state or federal compliance? Contact eqHR Solutions, one of the top HR companies in California.
State Changes
The year 2024 brings a tapestry of changes to employment laws across the United States, with each state weaving its unique set of regulations. From coast to coast, legislatures are responding to the evolving needs of the workforce, presenting employers and employees with a dynamic landscape of rights and responsibilities.
California
California, known for its progressive employment laws, is expected to further enhance worker protections in 2024. Employers can anticipate updates in areas such as wage and hour laws, paid family leave, and stricter regulations on worker misclassification.
Minimum Wage Changes
The State of California will see a new minimum wage of $16 per hour for non-exempt employees and $66,560 per year for salaried, exempt staff beginning in January. On top of that, several industries have also established new laws in regard to the minimum amount their employees can earn.
- Healthcare Workers: SB 525 raises the minimum wage to $25/hour for nearly all healthcare workers employed in California, regardless of whether they are paid on an hourly or salaried basis. This new law, which was signed by Governor Newsom in October of 2023, requires all healthcare employers to pay their workers no less than $25 per hour by June of 2028 and establishes the appropriate pay step increments allowable between now and that time.
- Fast Food Workers: AB 1228 increases the minimum wage for fast food workers to $20/hour, and establishes the potential for further increases in the following years. This new law applies only to organizations that are considered “national fast food chains”.

Paid Sick Leave
SB 616: Covid-19 changed everything we thought we knew about sick time. Since the recovery from the pandemic began, more and more California cities have opted to pass local Paid Sick Leave regulations, giving their workers additional options if they run out of sick time. The State of California has now stepped up to the plate and signed SB 616 into law on October 4, 2023. This new law expands the existing paid sick leave law (the Healthy Workplaces, Healthy Families Act of 2014) in many different ways.
Starting in 2024, employees will now be entitled to a minimum of 5 paid sick days per year instead of just 3 days. This will have a widespread effect on California businesses since virtually every California employee who works at least 30 days out of the year will benefit from the change.
Looking to outsource to HR companies in California? Contact eqHR Solutions, one of the leading HR providers for small and midsize businesses.
Unpaid Sick Leave
SB 848: Employees are now entitled to 5 days of unpaid protected leave for reproductive loss, making it illegal for employers to retaliate against their workers who take time off following the event. While employers are not required to pay their workers while they are out on this type of leave, the employee is entitled to use any sick or vacation time that is otherwise available to them based on company policies. The 5 days need to be taken within 90 days of the loss event. In rare cases where an individual experiences multiple loss events in the same year, the law also caps the number of days they can take to 20 total in any 12-month period.
SB 553: California becomes the first state to require employers to develop a workplace violence prevention program under this new law. In conjunction with OSHA and adding to already existing laws, this bill requires all employers to establish, implement, and maintain, at all times in all work areas, an effective workplace violence prevention plan containing specified information. It also requires the employer to record information in a violent incident log for every workplace violence incident, as specified. Furthermore, employers must also provide effective training to employees on the workplace violence prevention plan, among other things, and provide additional training when a new or previously unrecognized workplace violence hazard has been identified and when changes are made to the plan.
SB 699: Equips employees with new ways to challenge non-competes. On September 1, Governor Newsom signed a bill into law that prohibits employers from entering into non-competes with California employees that are void under state law, and also prohibits employers from attempting to enforce such agreements against their employees – regardless of whether the employee executed the agreement or worked in another state at the time.
AB 1076 creates non-compete notice requirements for employers. The governor signed another non-compete bill on October 13 that will implement a new burdensome notice requirement for employers, requiring them to notify current and former employees about unlawful non-compete covenants in their employment agreements.
Visit our blog page to learn more about California compliance from one of the top HR companies in California.
Colorado
Governor Jared Polis signed more than 470 new bills into law this year, with several affecting employers and workers alike. While some of these legislative moves will require only updating of company policies, others may require a bit of work on the employer’s end to ensure compliance.
The POWR Act (SB 23-172)
The POWR Act changes the former definition of unlawful “harassment”, as defined by the Colorado Anti-Discrimination Act (CADA). It also expands discrimination protection with regard to employment by adding “marital status” to the list of protected categories and creates new requirements for recordkeeping obligations.

Job Application Fairness Act (SB 23-158)
Beginning on July 1, 2024, employers will be prohibited from asking age-related questions to an applicant on a job application. This will include asking the individual to disclose their age, date of birth, or any attendance or graduation dates from school. The one exception to this new law is that employers can ask to verify that the applicant is compliant with age requirements imposed by federal law for some occupations.
Colorado Healthy Families and Workplace Act (SB 23-017)
The requirements for eligibility for leave of absence have been amended in this law, adding two new types of leave that must be allowed. Employees may now qualify for a leave of absence to grieve the death of a family member or due to evacuations caused by inclement weather.
Equal Pay for Equal Work Act (SB 23-105)
Amendments to this law will require employers to abide by stricter disclosure and notice requirements. These new requirements will include providing notice to employees about every job opportunity, along with the salary and benefit information that goes along with the role, and the application window to apply.
Connecticut
Connecticut is also expanding the appropriate use of paid sick time for employees. Employees in this state may now use paid sick time for attending to their emotional or psychological well-being, or if they are the parent or guardian of a child who is the victim of family violence or sexual assault (so long as they are not the alleged perpetrator).
For businesses operating in multiple states, it’s wise to consider the expertise of one of the top HR companies in California.
Florida
Gov. Ron DeSantis signed SB 1718 into law earlier this year, requiring employers with 25 or more employees to use the E-Verify system when completing the I-9 form. E-Verify is an internet-based system operated by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and the Social Security Administration that allows employers to electronically verify the employment eligibility of newly hired employees. This new law comes with hopes to help the state’s immigration issues.
Georgia

Georgia has passed SB 129 which has expanded employee rights for leave when they are voting. Prior to this law passing, employees were only entitled to two hours of time off to vote and only if they were unable to head to the polls outside of their normal working hours. But the new law allows for all employees to have a minimum of two hours off work, regardless of whether or not they need it to be able to make it to the polls in time.
Illinois
Paid Leave for all Workers
Starting January 1st SB 0208 will require employers to provide their employees up to 40 hours of paid leave per year. Employees must be employed for a minimum of 90 days before they are eligible to take the leave. The paid time off will accrue at a rate of 1 hour per every 40 hours worked. Employees can take the time away from work for whatever purpose they choose.
Kentucky
Kentucky became the 38th state in the US to legalize medical marijuana, bringing a host of new employment issues to businesses across the state. Under this new law, employers are not required to accommodate an employee’s use of the substance in the workplace but are allowed to maintain and enforce a zero-tolerance or drug-free workplace policy.
What does this mean for employers? Drug testing is still allowed, however, a drug test that is positive for marijuana can no longer be used against the employee in terms of claiming they are “under the influence”. Instead, employers must conduct behavioral assessments to determine whether or not their workers are “impaired”, and therefore unable to do their work.
Is your business operating in multiple states? Work with one of the top HR companies in California to ensure compliance.
Maryland
Medical Marijuana
Maryland has also joined the bandwagon, voting to legalize marijuana. However, the new law does not address any specifics as to how this would affect employers. We can anticipate these details in months to come.
Non-Compete Agreements
The state passed S.B. 591 which amends their previous statutes in regard to the provisions governing non-compete restrictions. The new law changes the threshold for which employees are affected. While the previous law prohibited non-competition agreements with employees making less than $15 per hour, while the new law changes that to anyone making less than 150% of the State’s minimum wage.
Massachusetts
Paid Family and Medical Leave
As expected, the state expanded the scope of paid family leave entitlements, eligibility criteria, and use of paid time off while on leave. The new law requires employers to allow their employees to supplement their paid family leave benefits with any PTO they have accrued, however, it also states that an employer is prohibited from requiring the employee to use any hours available. The update to the law also increased the percentage of eligible wages that are used to calculate the contribution rate, thus increasing the maximum weekly benefit amount that employees are eligible to receive.
Michigan
Right to Work Law Repealed
The state recently became the first state in decades to repeal its Right to Work law with regard to unions. This means that in unionized workplaces in Michigan can now require their workers to join the union and pay dues as a condition of their employment.
Contact one of the top HR companies in California with any questions you might have about workplace compliance.
Minnesota
Paid Family and Medical Benefit Insurance Program
Minnesota and five other states now join the eleven states with existing Paid Family Medical Benefit programs. While FMLA provides protection for employees while on leave, it does not require the time away from work to be paid. These states – now 17 in total – have implemented programs that will also provide some income for the employee while they are tending to their medical needs. While H.F. 2 doesn’t go into full effect until 2026, employer reporting is set to begin in July of 2024.
Montana

Free Speech Protection
Montana has passed S.B. 270 which protects employee’s rights to freedom of speech in the workplace. Employers are now prohibited from firing individuals for engaging in legal expressions of free speech, including on social media, unless it specifically violates the employer’s policies or contracts.
New York
Focus on Pay Equity
In an effort to further pay transparency trends, New York employers must now include a compensation range in all job postings, including promotions and transfer opportunities.
Oregon
Leaves of Absence
Several new laws in the state of Oregon will impact employers when it comes to people who are eligible for a leave of absence. Oregon HB 3443 expanded eligibility to include bias crime victims, and Oregon SB 1033 better defines what active service of the state is when it comes to military leaves.
Workplace Safety
Oregon SB 907 now bans employers from discriminating or retaliating against any employee who refuses to work if they believe in good faith that the work would cause them to be exposed to hazardous conditions.
Child Support
Oregon SB 184 now extends an employer’s responsibility to report individuals who work for them for the purpose of collecting child support to include independent contractors.
Is your business compliant with state and federal regulation? Contact eqHR, one of the leading HR companies in California, for a comprehensive overview of your compliance.
Rhode Island
The state of Rhode Island has increased the penalties for wage and hour violations. Rhode Island HB 5902 also increased the fines associated with employee misclassification.
Texas
Texas employers are now required to post notices informing their employees about instances of workplace violence. HB915 states that these notices must go up regardless of the business size, and must be posted any time there is any form of violence or suspicious activity in the workplace.
Washington

Unemployment Regulations
New laws will go into effect on January 1, 2024 regarding unemployment benefits and who can claim them when they become unemployed.
Washington SB 5176 now makes it so that any owner or corporate officer who has a family member that is an owner of 10% or more of the company cannot be eligible for unemployment benefits unless the company is dissolved or the individual relinquishes all ownership rights.
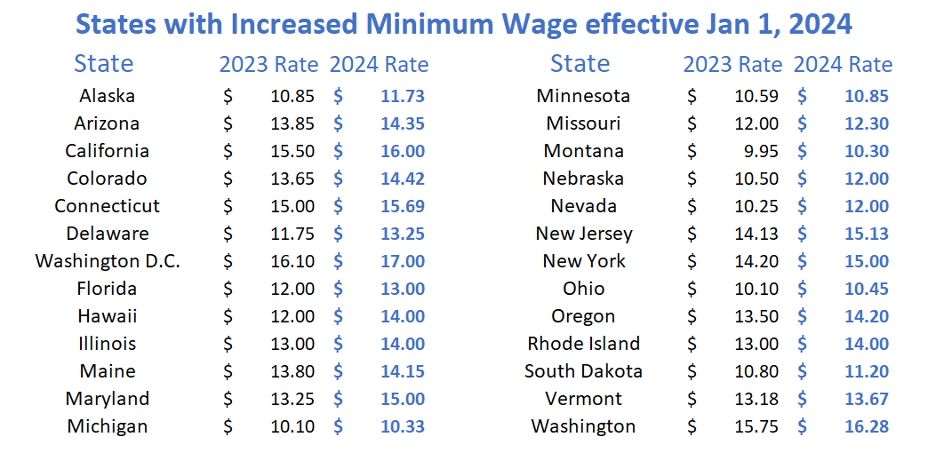
State Minimum Wage Increases
In addition to these new regulations, 26 states will have an increase in their minimum wage effective January 1, 2024. Many states adjust their rates on an annual basis based on inflation, while others simply raise the threshold when they see it as necessary. The chart below shows which states will see an increase this coming year.
Contact eqHR Solutions to outsource to one of the top HR companies in California.
A Look at What is Still to Come
Many states and Federal agencies still have some new laws in the works and have yet to roll them out. These changes can be anticipated for mid-2024 or the start of 2025 in many areas.
Remote Work Policies:
With the continued prevalence of remote work, federal lawmakers are expected to address the challenges and opportunities presented by this shift. We can anticipate new regulations providing guidelines for remote work arrangements, data security standards, and efforts to strike a balance between flexibility and accountability in the virtual workplace.
Equal Pay and Pay Equity:
The pursuit of pay equity remains a top priority at the federal level. In 2024, enhanced equal pay legislation is expected to be enacted, requiring businesses to provide greater transparency regarding salary structures. Employers will need to justify any pay discrepancies and demonstrate a commitment to fair and equitable compensation.
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Initiatives:
As diversity and inclusion become integral aspects of modern-day corporate culture, lawmakers are pushing for concrete measures to promote workplace diversity. Expect to see requirements for federal contractors to implement diversity and inclusion programs, set targets, and report on progress toward inclusive workplaces.
Learn more about how to prioritize DE&I initiatives from one of the top HR companies in California.
Focus on Mental Health Support:
Recognizing the importance of mental health in the workplace, federal legislation will address the need for mental health support. This could involve requirements for employers to provide resources, flexible work arrangements, accommodations, and awareness programs to prioritize the well-being of their workforce and destigmatize mental health issues within the workplace.
Tech and Data Privacy:
As technology continues to shape the modern workplace and we become more reliant on it to operate businesses, federal laws must also evolve to address data privacy concerns. Expect new regulations outlining guidelines for the collection, storage, and use of employee data, with a focus on protecting individual privacy rights.
Expansion of Family and Medical Leave:
Federal family and medical leave laws will likely see further expansion in 2024, with proposals to increase the duration of leave, broaden eligibility criteria, and potentially introduce paid leave provisions. Employers should stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and accommodate the evolving needs of their workforce.
Employee Classification in the Gig Economy:
The gig economy and worker classification have been ongoing areas of concern. This unique micro-economy has blurred traditional employment lines, leading to debates over worker classification. In 2024, federal lawmakers plan to introduce measures to clarify the classification of gig workers, potentially impacting benefits, wages, and other employment-related considerations. This could have a huge impact on businesses since many started moving towards gig employment following COVID.
See why eqHR Solutions is one of the top-rated HR companies in California.
Automation and Job Displacement:
The rise of automation has prompted concerns about job displacement. Employment laws in 2024 will likely address these challenges by requiring companies to implement retraining programs, provide support for displaced workers, and navigate the ethical considerations surrounding the use of artificial intelligence in the workplace.
Enhanced Worker Protections:
Federal employment laws are likely to strengthen worker protections in various areas. This may include updates to occupational safety standards, anti-discrimination laws, and whistleblower protections. Employers should stay vigilant to changes that impact workplace safety and employee rights.
COVID-19 Implications:
The ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic may result in continued legislative measures to address workplace safety, remote work accommodations, and employee rights in the context of public health emergencies.
Outsource to HR Companies in California
As workplaces become more modern and employment laws change, employers are tasked with remaining compliant and anticipating the impacts on their business. It is critical for leadership to stay informed, be proactive, and ensure their workplace culture is one that is aligned with the many changes that happen each year.
Employers operating in multiple states must be even more diligent in staying on top of changing laws, adjusting policies accordingly, and fostering a workplace culture that aligns with the diverse legal frameworks across the nation. By proactively addressing these changes, businesses can successfully navigate the new state employment laws and ensure compliance in this dynamic era.
Want to make sure your business is compliant with all the changing laws? Contact eqHR today to schedule a complete assessment with one of the top HR companies in California!

 Understanding California Paid Family Leave: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding California Paid Family Leave: A Comprehensive Guide How California Payroll Audit Consulting Services Can Boost Your Small Business in 2025
How California Payroll Audit Consulting Services Can Boost Your Small Business in 2025 How California Payroll Audit Consulting Services Can Help Mitigate Risk in 2025's Economic Uncertainty
How California Payroll Audit Consulting Services Can Help Mitigate Risk in 2025's Economic Uncertainty